

| Version for distribution: | |||
| 6.94b | software updates and changes | purchase a license | download | workshops | publications | feedback |
AOMix is a user-friendly software for the molecular orbital (MO) analysis. It calculates the MO compositions in terms of the constituent chemical fragments (you can specify them as atoms, groups of atoms, atomic orbitals, fragment molecular orbitals, groups of atomic orbitals, etc.) in the molecule or atom. AOMix automatically processes output files of multiple quantum-chemical packages (see the list below). AOMix also allows you to analyze chemical structure (bonding/antibonding nature of molecular orbitals) using overlap populations (total and per molecular orbital), valence indices, 2-center (Mayer, Lowdin, Wiberg, and bond-order symmetry components) and 3-, 4-, 5- and 6-center bond orders,
probing of molecular orbital contributions to bonding using orbital occupancy-perturbed Mayer bond orders (OOPBOs); charge decomposition analysis, CDA (total, per molecular orbital, per symmetry type), and condensed Fukui functions. 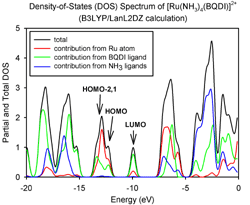
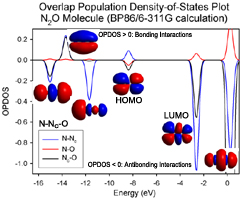
AOMix generates total, partial, and overlap population density-of-states (DOS) plots (these are available in line-plot and continuous-plot representations, see Figures 1, 2, and 3). Overlap population DOS plots are also refered in the literature as Crystal Orbital Overlap Population (COOP) diagrams.
A very important part of quantum chemical research is to interpret the results in terms of qualitative concepts. This software was developed to help in the analysis of the nature of the chemical bonding in molecular systems and to monitor changes in the electron density distribution upon the electron excitation. Let's say, there is a band in an absorption spectrum of a molecule or an ion at 400 nm which is assigned to a HOMO -> LUMO+2 electron excitation. What does it tell us about properties of this molecule/ion? What do we know about the nature of the corresponding excited state? What will happen with this molecule / ion after the photoexcitation? AOMix helps to answer these questions.
With AOMix, you can
- generate wave functions of multi-fragment molecular systems from converged fragment wave functions (any spin state and spin coupling);
- analyze molecular orbital compositions in terms of fragment atomic/molecular orbitals;
- evaluate bonding / antibonding contributions of molecular orbitals to the electronic structure (using overlap populations);
- calculate the amount of electron donation and back-donation between molecular fragments (using the charge decomposition analysis, CDA, implemented in the AOMix-FO module);
- create total, partial and overlap population density-of-states plots;
- calculate condensed Fukui functions;
- evaluate charge transfer characters of electronic transitions;
- calculate the total and free valence index for atoms or fragments;
- calculate the two-center (Mayer, Wiberg, Lowdin) and multi-center bond orders between molecular fragments;
- probe molecular orbital contributions to bonding using orbital occupancy-perturbed Mayer bond orders (OOPBOs);
- simulate UV-Vis absorption spectra from Gaussian TD-DFT calculations.
AOMix
calculates the Wiberg bond order indices between molecular fragments (calculated in the canonical orbital basis: (P*S) x (P*S) and in the orthonormal Lowdin orbital basis);
calculates the Mayer bond orders (including the bond order contributions from alpha- and beta-spin occupied orbitals for open-shell systems) between molecular fragments;
if molecular symmetry is present, calculates symmetry components (for each irreducible representation) of Mayer bond orders (including the bond order contributions from alpha- and beta-spin MOs for open-shell systems) between fragments. Symmetry decomposition of bond orders helps in picturing electronic structure and contributions to chemical bonding;
calculates total and free valence of atoms / fragments;
calculates the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of the AO overlap matrix;
performs Lowdin population analysis (LPA);
calculates the 3-, 4-, 5- and 6-center bond order indices between molecular fragments to help in finding possible multi-center orbital interations.
AOMix output files also contain:
- Lowdin and Mulliken alpha-spin electron populations,
- Lowdin and Mulliken beta-spin electron populations,
- Lowdin and Mulliken gross electron populations,
- Lowdin and Mulliken spin densities,
- (for spin-unrestricted calculations) the overlap matrix between beta-spin molecular orbitals and alpha-spin molecular orbitals (the so-called mutual overlap matrix).
Here is one of the AOMix output files. In this example, fragments are defined by automatically by the program (each atom is a fragment).
In addition, if each atom is a fragment, AOMix writes two UCSF Chimera attribute files. The first file (with the atomic attributes) allows easy visualization of the calculated atom-based properties:
- atomic charges,
- MPA, NPA and LPA spin densities,
- total and free valence indices of atoms.
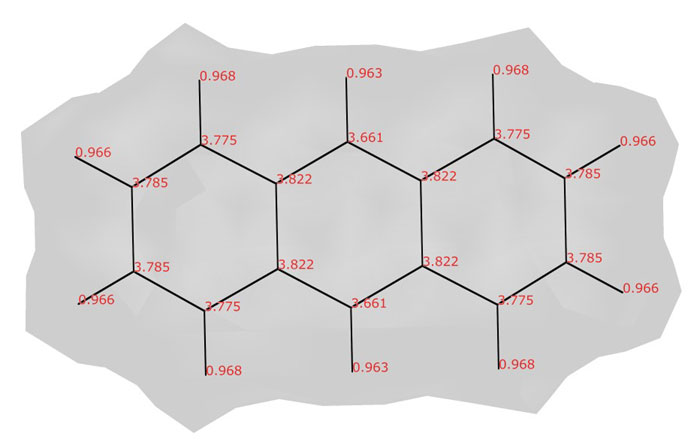
Atomic valence indices in the anthracene molecule (C14H10)
The second file (with the PseudoBond attributes) allows easy visualization of the calculated two-center properties:
- Lowdin and Wiberg bond orders,
- Mayer bond orders and its components.
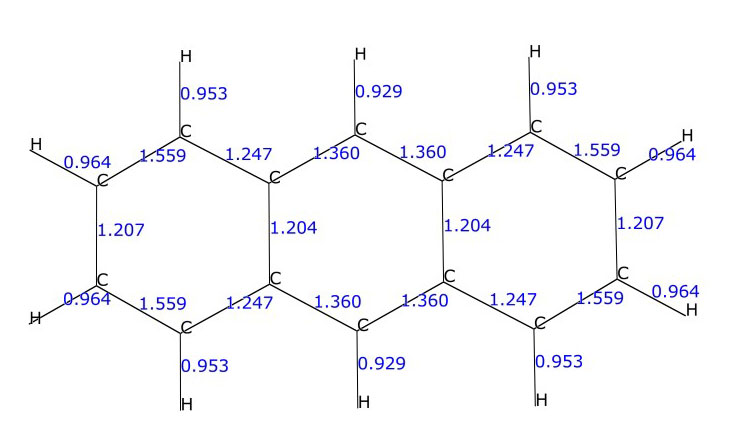
Mayer bond orders for the C-C and C-H bonds in the anthracene molecule (C14H10)
AOMix also prints the S0.5 x P x S0.5 matrix for alpha- and beta-spin orbitals.
AOMix can be also used to recover the initial guess from the computed wave function (see Appendix I of the AOMix manual).
AOMix provides:
- the MO composition analysis in terms of
- ALL atomic orbitals in one run (number of fragments = number of molecular orbitals);
- ALL atoms in one run (number of fragments = number of atoms), these include the automatic s,p,d,f,g-orbital contribution breakdown (see the example);
- or any large number of molecular fragments (defined as a list of atoms or/and atomic orbitals);
- total and partial density-of-states (TDOS and PDOS) plot data (both continuos and line plots are available);
- overlap populations density-of-states (OPDOS) plot data;
- MS Windows and UNIX scripts for Gaussian CUBE file generation;
- in addition to the regular AOMix output file (for atoms as individual fragments and for atomic orbitals as individual fragments), the HTML file (AOMix-MPA-orb.html) is generated. It contains the information about MO compositions in terms of MOST IMPORTANT atomic orbitals (6 largest contributions with values greater than 0.5%)
You can refer to the AOMix manual and these publications to learn about the AOMix capabilities.
|
|
- Mulliken population analysis (MPA)
- modified Mulliken population analysis (MMPA)
- C2 population analysis (SCPA)
- Lowdin population analysis (LPA)
- charge decomposition analysis (CDA) (using AOMix-FO)
Supported operating systems AOMix MS Windows 2000, XP + MS Windows Vista, 7, 8, 9, 10 + (*) Linux, MacOS + (**) *) For processing of ADF, DFTB+, GAMESS(US), Gaussian, Jaguar, ORCA, Q-Chem and Turbomole output files only.
**) AOMix can be run under these operating systems using any Windows emulator (such as WINE or any other of your choosing).
|
|
Compositions of molecular orbitals, overlap populations between molecular fragments, bond orders and density-of-states spectra were calculated using the AOMix program [1,2].
- S. I. Gorelsky, AOMix: Program for Molecular Orbital Analysis, http://www.sg-chem.net/, version X.X, 2019.
- S. I. Gorelsky, A. B. P. Lever, J. Organomet. Chem. 2001, 635, 187-196.
|
|
 |
ADF (Scientific Computing & Modelling NV).
AOMix has been tested with the following versions: ADF 2004.01, ADF 2005.01, ADF 2012.01; please note that ADF calculations with core functions (do not confuse core functions with core orbitals!) cannot be processed by the current version of AOMix. |
| CNDO/INDO | CNDO/INDO (by J.R. Reimers, University of Sydney, Australia)
|
| DFTB+ | DFTB+ (by Density Functional based Tight Binding with a lot of extensions)
AOMix has been tested with the following versions: Release: 1.1; 1.3 |
 |
The General Atomic and Molecular Electronic Structure System
GAMESS from Iowa State University and PC GAMESS / FIREFLY from Moscow State University.
AOMix has been tested with the following versions: GAMESS VERSION = 12 JAN 2009 (R3); GAMESS VERSION = 18 AUG 2016 (R1); PC GAMESS version 7.0, FireFly 8.0.0 |
 |
Gaussian 98, Gaussian 03, Gaussian 09 and Gaussian 16 (Gaussian, Inc.) |
 |
HyperChem 4.x-7.x (HyperCube, Inc.) |
 |
Jaguar (Schrodinger, Inc.).
AOMix has been tested with the following versions: Jaguar 7.6, 7.9, and 8.3 |
| MOPAC2009 (James J. P. Stewart, Stewart Computational Chemistry)
AOMix has been tested with the following versions: MOPAC2009, Version 8.311W. |
|
 |
ORCA (Department of molecular theory and spectroscopy, Max Planck Institute for Chemical Energy Conversion, Muelheim/Ruhr, Germany)
AOMix has been tested with the following versions: ORCA 3.0.1 and ORCA 4.0.1 |
 |
Q-Chem (Q-Chem, Inc.).
AOMix has been tested with the following versions: Q-Chem 3.2, Q-Chem 4.0, Q-Chem 4.3, Q-Chem 5.0 |
 |
Spartan (Wavefunction, Inc.).
AOMix has been tested with the following versions: Spartan '02, Spartan '03, and Spartan '06. |
| Turbomole | Turbomole (COSMOlogic).
AOMix has been tested with the following versions: Turbomole 6.5 and 6.6 |
| ZINDO | ZINDO (by M.C. Zerner, Quantum Theory Project, University of Florida;
ZINDO is available in Cerius2 (Accelrys Inc.)
and CAChe (CAChe Group, Fujitsu)); AOMix has been tested with the following versions: ZINDO 98.1 and ZINDO 99.1 |